What is Plant Cell Chloroplasts | Structure and Function of Chloroplasts
What are Chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are unique structures found in plant cells that specialize in converting sunlight into energy that plants can use. This process is called photosynthesis.
Organelle
Chloroplasts are considered as organelles in plant cells. Organelles are special structures in cells that perform specific functions. The main function of chloroplasts is photosynthesis.
Get Free Counseling
Chloroplast Structure
Most chloroplasts are oval drops, but they can come in all sorts of shapes like stars, cups, and ribbons. Some chloroplasts are relatively small compared to the cell, while others can take up most of the space inside the cell.
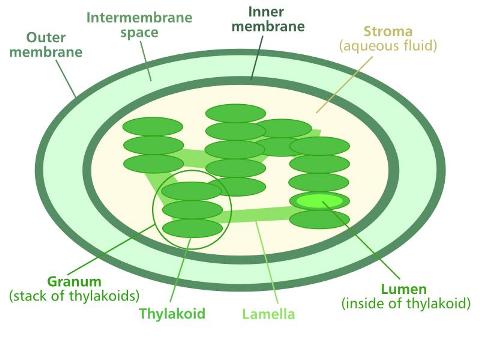
Outer Membrane – The outer surface of the chloroplast is protected by a smooth outer membrane.
Inner Membrane – Just inside the outer membrane is the inner membrane that controls which molecules can move in and out of the chloroplast. The outer membrane, the inner membrane, and the fluid between them form the envelope of the chloroplast.
Substrate – The substrate is the liquid inside the chloroplast where other structures such as thylakoids float.
Thylakoids – Floating in the substrate is a collection of chlorophyll-containing vesicles called thylakoids. The thylakoids are usually arranged in stacks called granums, as shown in the figure below. The granums are connected by disc-like structures called lamellae.
Pigment – Pigment that gives chloroplasts and plants its color. The most common pigment is chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color. Chlorophyll helps absorb energy from the sun.
Other – Chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes to make proteins from RNA.
Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts use photosynthesis to turn sunlight into food. Chlorophyll captures energy from light and stores it in a special molecule called ATP (short for Adenosine Triphosphate). Then, ATP is combined with carbon dioxide and water to make sugars like glucose that plants can use as food.
Other Functions
Other functions of chloroplasts include fighting disease as part of a cell’s immune system, storing energy for cells, and making amino acids for cells.
Interesting Facts about Chloroplasts:
Single cells, like those found in algae, may have only one or two chloroplasts. However, more complex plant cells can contain hundreds of cells.
Chloroplasts sometimes move around the cell to locate themselves where they can best absorb sunlight.
The word “chloro” in chloroplasts comes from the Greek word chloros (meaning green).
The most abundant protein in chloroplasts is the Rubisco protein. Rubisco is perhaps the most abundant protein in the world.
Human and animal cells do not need chloroplasts because we get energy by eating and digesting food rather than by photosynthesis.
Scientists estimate that there are about 500,000 chloroplasts in a square millimeter of leaf.
There are actually many different colors of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll A is the most common and is green in color. Chlorophyll C is yellow or brownish in color.