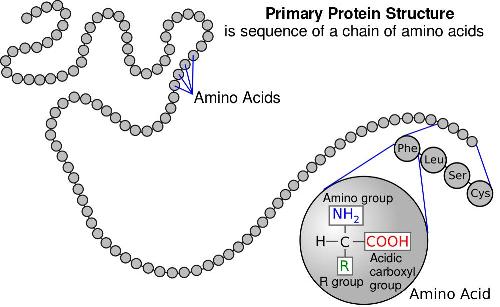
Amino acids are special organic molecules used by living organisms to make proteins. The main elements of amino acids are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. There are 20 different amino acids that combine to make proteins in our bodies. Our bodies can actually produce some amino acids, but the rest must be obtained from our diet.
Proteins are long chains of amino acids. There are thousands of different proteins in the human body. They provide all kinds of functions to help us survive.
Protein is essential for life. About 20% of our body is made up of protein. Every cell in our body uses protein to perform functions.
Proteins are made inside cells. When a cell makes proteins, it is called protein synthesis. The instructions for making proteins are contained in the DNA molecules inside the cell nucleus. The two main steps in the process of making proteins are called transcription and translation.
The first step in making proteins is called transcription. This is when the cell makes a copy (or “transcription”) of DNA. The copy of DNA is called RNA because it uses another type of nucleic acid called ribonucleic acid. RNA is used in the next step, called translation.
The next step in making proteins is called translation. This is when RNA is converted (or “translated”) into a sequence of amino acids that make up a protein.
Translation to make new proteins from RNA instructions takes place in a complex machine in the cell called the ribosome. The following steps take place in the ribosome.
- RNA moves to the ribosome. This type of RNA is called “messenger” RNA. It is abbreviated as mRNA where the “m” is for messenger.
- mRNA attached to the ribosome. The ribosome determines where to start on the mRNA by looking for a special three-letter “start” sequence called a codon.
- Then the ribosome moves down the mRNA strand. Every three letters represents another amino acid molecule. Ribosomes build amino acid sequences based on the mRNA code.
- When the ribosome sees the “stop” code, it completes the complete protein and translation process. How a ribosome makes a protein
Different Types of Proteins:
There are literally thousands of different proteins in our bodies. Here are some of the main groups and functions of proteins:
- Structure – Many proteins provide structure to our bodies. This includes collagen found in cartilage and tendons.
- Defense – Protein helps protect us from disease. They form antibodies against foreign invaders such as bacteria and other harmful substances.
- Transport – Protein can help transport essential nutrients throughout our body. An example is the oxygen-carrying hemoglobin in our red blood cells.
- Catalysts – Some proteins, such as enzymes, act as catalysts to facilitate chemical reactions. They help us break down and digest food so our cells can use it.
- We get amino acids from staple foods like chicken, bread, milk, nuts, fish and eggs. Hair is made up of a protein called keratin.
- A special type of RNA called a carrier RNA moves amino acids to the ribosome.
- It is abbreviated as tRNA where the “t” stands for transfer.
- The bonds between the amino acids of a protein are called peptide bonds.
- The different arrangement and type of amino acids along the protein strand determines the function of the protein.

