What are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria are important parts of our cells because they make energy from food that the rest of the cell can use.
Organelle
Animals and plants are made up of many complex cells called eukaryotic cells. Inside these cells are structures that perform specific functions for the cell called organelles. The organelle responsible for the production of energy for the cell is the mitochondria.
How many mitochondria are in a cell?
Different types of cells have different numbers of mitochondria. Some cells simply contain only one or two mitochondria. However, complex, energy-intensive animal cells, like muscle cells, can have thousands of mitochondria.
Energy Factory
The main function of mitochondria is to produce energy for the cell. Cells use a special molecule for energy called ATP. ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate. ATP for the cell is produced in the mitochondria. You can think of mitochondria as the energy factory or powerhouse of the cell.
Respiration
Mitochondria produce energy through cellular respiration. Mitochondria take food molecules in the form of carbohydrates and combine them with oxygen to produce ATP. They use proteins called enzymes to create the correct chemical reaction.
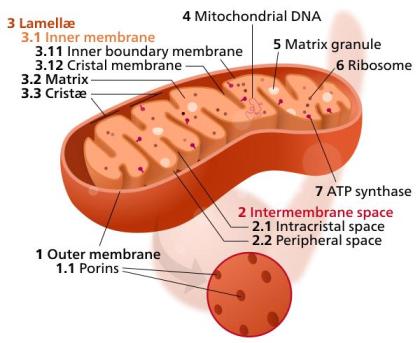
Mitochondrion Structure
Mitochondria have a distinct structure that helps them generate energy.
Outer Membrane – The outside is protected by a smooth outer membrane and varies in shape from round teardrop to long rod.
Inner Membrane – Unlike other organelles in the cell, mitochondria also have an inner membrane. The inner membrane is pleated with many folds and performs several functions that help generate energy.
Cristae – The folds of the inner membrane are called cristae. Having all these folds increases the surface area of the inner membrane.
Matrix – The matrix is the space inside the inner membrane. Most of the proteins in the mitochondria are found in the matrix. The substrate also contains ribosomes and mitochondrial-specific DNA.
Other Functions
In addition to energy production, mitochondria perform other functions for the cell, including cellular metabolism, the citric acid cycle, thermogenesis, the control of calcium levels, and the production of certain steroids.
Interesting Facts about Mitochondria:
They can quickly change shape and move around the cell as needed.
When the cell needs more energy, the mitochondria can reproduce by growing and then dividing. If the cell needs less energy, some of the mitochondria will die or become inactive.
Mitochondria are very similar to some bacteria. For this reason, some scientists believe that it was initially absorbed by bacteria by more complex cells.
Different mitochondria make different proteins. Some mitochondria can make hundreds of different proteins that are used for different functions.
In addition to energy in the form of ATP, they also produce small amounts of carbon dioxide.