The United States is often divided into geographical regions. These regions help group and describe larger regions or states that share characteristics such as geography, culture, history, and climate.
There are also some official government areas, such as the United States, where the Census Bureau and standard federal areas are used, but most people use the five major areas when dividing states. These are Northeast, Southeast, Midwest, Southwest, and West.
These are not officially defined regions, so some border states may appear in different regions depending on the document or map you are viewing. For example, Maryland is sometimes considered part of the Southeast, but the map includes it in the Northeast.
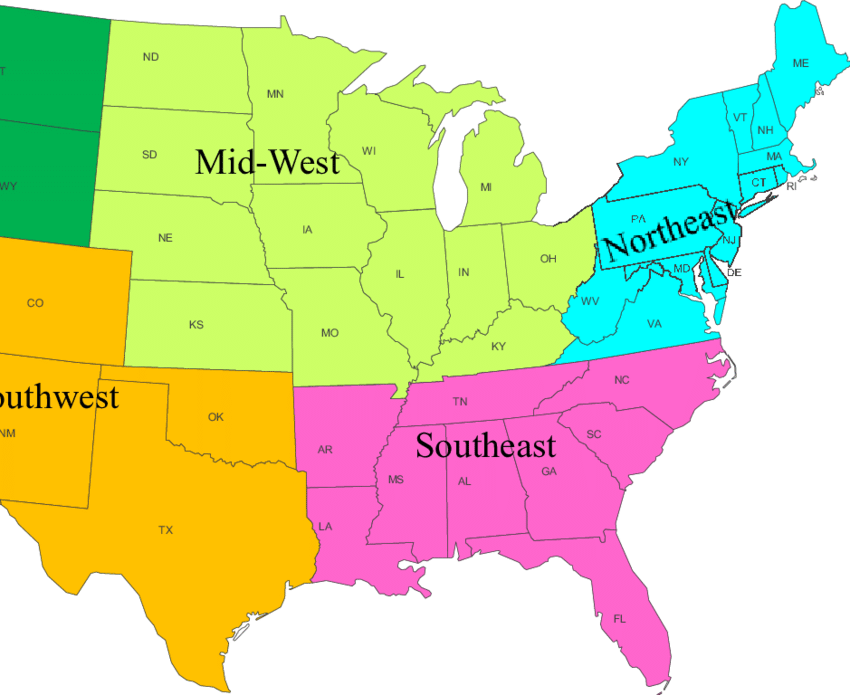
States include: Maine, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Hampshire, Vermont, New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland
Climate: Humid continental climate with cool summers in the northernmost regions. It snows in winter as temperatures regularly drop below freezing.
Key geographic features: Appalachian Mountains, Atlantic Ocean, Great Lakes, borders Canada to the north
States included: West Virginia, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Arkansas, Louisiana, Florida
Climate: Humid subtropical climate with hot summers. Hurricanes can reach landfall in the summer and fall months along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts.
Major geographical features: Appalachian Mountains, Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, Mississippi River
States included: Ohio, Indiana, Michigan, Illinois, Missouri, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Kansas, Nebraska, South Dakota, North Dakota
Climate: Humid continental climate throughout most of the region. Snow is common during the winter, especially in the northern areas.
Major geographical features: Great Lakes, Great Plains, Mississippi River, borders Canada to the north
States included: Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Arizona
Climate: Semiarid Steppe climate in the western area with a more humid climate to the east. Some of the far western areas of the region have an alpine or desert climate.
Major geographical features: Rocky Mountains, Colorado River, Grand Canyon, Gulf of Mexico, borders Mexico to the south.
States included: Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, Idaho, Washington, Oregon, Utah, Nevada, California, Alaska, Hawaii
Climate: A range of climates including semiarid and alpine along the Rocky and Sierra Mountains. The coastline in California is a Mediterranean climate. Desert climates can be found in Nevada and Southern California.
Major geographical features: Rocky Mountains, Sierra Nevada Mountains, Mohave Desert, Pacific Ocean, borders Canada to the North and Mexico to the south
Here are some other commonly referenced sub-regions:
Mid-Atlantic – Virginia, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, New Jersey
Central Plains – Iowa, Missouri, Kansas, Nebraska
Great Lakes – Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, Michigan
New England – Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut
Pacific Northwest – Washington, Oregon, Idaho
Rocky Mountains – Utah, Colorado, New Mexico, Wyoming, Montana

