Enzymes are special proteins. Like all proteins, enzymes are made up of chains of amino acids. Enzyme function is determined by the amino acid sequence, the amino acid type, and the shape of the chain.
Enzymes are responsible for much of the work that happens in the cell. They act as catalysts that help create and speed up chemical reactions. When a cell needs to do something, it almost always uses an enzyme to speed things up.
Enzymes are very specific. This means that each enzyme only reacts with the specific substance for which it is designed. This is important so that the enzymes don’t go wrong and cause chemical reactions they shouldn’t.
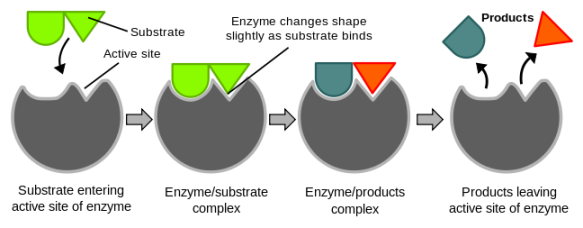
Enzymes have a special pocket on their surface called the “active point”. The molecule with which they were supposed to react fits perfectly in this bag. The molecule or substance with which the enzyme reacts is called a “substrate”.
The reaction takes place between the enzyme and the substrate at the active site. After the reaction is finished, the new molecule or substance is released by the enzyme. This new substance is called a “product”.
Things that Affect Enzyme Activity
The enzyme and substrate medium can affect the rate of the reaction. In some cases, the environment can prevent enzymes from working or even breaking down. When an enzyme stops working, we call it “denaturation”. Here are some things that can affect enzyme activity:
-
- Temperature – Temperature can affect the reaction rate. The higher the temperature, the faster the reaction. However, at some point the temperature gets so high that the enzyme will be denatured and stop working.
-
- pH – In many cases, the pH, or acidity, of the environment surrounding the enzyme and the substrate can affect the rate of a reaction. Extremely high pH (high or low) will often slow down or even stop the reaction altogether.
-
- Concentration – Higher concentrations of substrates or enzymes can speed up the reaction.
- Inhibitors – Inhibitors are molecules specifically designed to block the action of enzymes. They can only slow down the reaction or stop it altogether. Some inhibitors bind to the enzyme causing it to change shape and not work properly. The opposite of an inhibitor is an activator that can help speed up a reaction.
- Enzymes don’t run out after doing their job. They can be used many times.
- Many drugs and toxins act as enzyme inhibitors.
- Some snake venoms are inhibitors. Enzymes are commonly used in industrial applications such as food processing, papermaking, and detergents.
- There is an enzyme in saliva called amylase that helps break down starches when you chew.
- Enzymes play an important role in breaking down our food so that our bodies can use it. There are special enzymes to break down different foods. They are found in our saliva, stomach, pancreas and small intestine.

